Configurando OTRS com PSGI/Plack e executando com Starman
Nesse artigo vou mostrar como configurar OTRS usando PSGI/Plack. Na versão 5.0.12 do OTRS existe um arquivo com PSGI/Plack, mas não funciona por ser algo experimental. Criei um arquivo com PSGI/Plack para executar o OTRS e depois executar com Starman.
[ Hits: 6.113 ]
Por: Lucas em 05/10/2016
Execução
Renomear:
cd otrs/bin/cgi-bin
mv app.psgi app.psgi.old
Criar:
touch app.psgi
Depois de criado, abra com editor de sua preferência e adicione o código abaixo:
use Plack::App::File;
use CGI::Emulate::PSGI;
use CGI::Compile;
my $path_of_otrs = "/caminho_do_diretorio/otrs";
my $cgi_script_index = $path_of_otrs . "/bin/cgi-bin/index.pl";
my $sub_index = CGI::Compile->compile($cgi_script_index);
my $app_index = CGI::Emulate::PSGI->handler($sub_index);
my $cgi_script_customer = $path_of_otrs . "/bin/cgi-bin/customer.pl";
my $sub_customer = CGI::Compile->compile($cgi_script_customer);
my $app_customer = CGI::Emulate::PSGI->handler($sub_customer);
my $cgi_script_installer = $path_of_otrs . "/bin/cgi-bin/installer.pl";
my $sub_installer = CGI::Compile->compile($cgi_script_installer);
my $app_installer = CGI::Emulate::PSGI->handler($sub_installer);
my $cgi_script_nph_genericinterface = $path_of_otrs . "/bin/cgi-bin/nph-genericinterface.pl";
my $sub_nph_genericinterface = CGI::Compile->compile($cgi_script_nph_genericinterface);
my $app_nph_genericinterface = CGI::Emulate::PSGI->handler($sub_nph_genericinterface);
my $cgi_script_public = $path_of_otrs . "/bin/cgi-bin/public.pl";
my $sub_public = CGI::Compile->compile($cgi_script_public);
my $app_public = CGI::Emulate::PSGI->handler($sub_public);
my $cgi_script_rpc = $path_of_otrs . "/bin/cgi-bin/rpc.pl";
my $sub_rpc = CGI::Compile->compile($cgi_script_rpc);
my $app_rpc = CGI::Emulate::PSGI->handler($sub_rpc);
builder {
mount "/" => $app_index;
mount "/index.pl" => $app_index;
mount "/customer.pl" => $app_customer;
mount "/installer.pl" => $app_installer;
mount "/nph-genericinterface.pl" => $app_installer;
mount "/public.pl" => $app_public;
mount "/rpc.pl" => $app_rpc;
mount "/otrs-web" => Plack::App::File->new(root => $path_of_otrs . '/var/httpd/htdocs')->to_app;
};
Código no meu gitHub:
Não esqueça de alterar o 'caminho_do_diretorio' no código acima.
Agora, vamos executar:
starman app.psgi
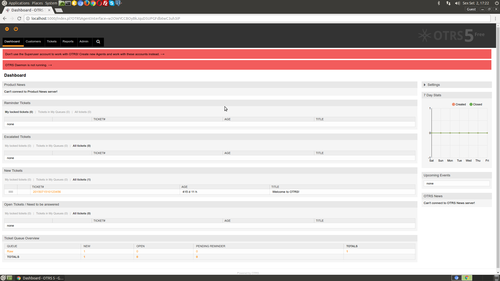
Por padrão, o Starman executa na porta 5000, então para testar o OTRS, abra seu navegador e digite o endereço:
http://localhost:5000
Executando o Starman em outra porta, com um número maior de processos e criando pid:
starman --l :2222 app.psgi --workers 5 --daemonize --pid app.pid
No exemplo acima, executa o Starman na porta 2222, com 5 processos e pid no arquivo "app.pid".
Matando os processos:
cat app.pid | sudo xargs kill
Configurando Apache com Proxy Reverse
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
ServerName meudominio.com
ServerAlias meudominio.com www.meudominio.com
<Location />
ProxyPass http://localhost:2222/
ProxyPassReverse http://localhost:2222/
</Location>
</VirtualHost>
Configurando Nginx com Proxy Reverse
server_name meudominio.com www.meudominio.com;
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
root /var/www/html;
index index.html index.htm;
location / {
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_pass http://localhost:2222;
}
}
Conclusão
A intenção desse artigo, foi ensinar como configurar OTRS com PSGI/Plack e executar com Starman. Demais configurações do OTRS, você deve seguir o link abaixo:Resultado da instalação: Espero ter ajudado.
Obrigado.
2. Execução
Executando os principais frameworks Perl no cPanel com CGI
Catalyst Framework Perl - (parte 2)
Catalyst Framework Perl (parte 1)
Catalyst Framework Perl - Parte III
Módulos CPAN no Debian e distros GNU/Linux em geral
Executando os principais frameworks Perl no cPanel com CGI
A forma correta de se instalar módulos Perl
Programando uma Intranet com Apache, MySQL e Perl (parte 2)
Decodificando filmes do programa "3w player"
ola amigo... ótimo artigo.. segui ele consegui fazer a instalação certinho... sem nenhum problema..
só não achei a senha para acessar o OTRS depois que completa a instalação..
Qual é o usuário e senha padrão?
Grato
[1] Comentário enviado por gugarasta em 07/10/2016 - 17:40h
ola amigo... ótimo artigo.. segui ele consegui fazer a instalação certinho... sem nenhum problema..
só não achei a senha para acessar o OTRS depois que completa a instalação..
Qual é o usuário e senha padrão?
Grato
User: root@localhost
Pass: root
[2] Comentário enviado por mineirobr em 07/10/2016 - 18:31h
[1] Comentário enviado por gugarasta em 07/10/2016 - 17:40h
ola amigo... ótimo artigo.. segui ele consegui fazer a instalação certinho... sem nenhum problema..
só não achei a senha para acessar o OTRS depois que completa a instalação..
Qual é o usuário e senha padrão?
Grato
User: root@localhost
Pass: root
Deu certo... muito obrigado amigão.
E possível instalar OTRS 5 no linux, com banco de dados esterno sql server?
[4] Comentário enviado por pauloirus em 29/03/2017 - 17:41h
E possível instalar OTRS 5 no linux, com banco de dados esterno sql server?
Sim é possivel, veja o arquivo Karnel/Config.pm
# The database DSN for Microsoft SQL Server - only supported if OTRS is
# installed on Windows as well
# $Self->{DatabaseDSN} = "DBI:ODBC:driver={SQL Server};Database=$Self->{Database};Server=$Self->{DatabaseHost},1433";
Patrocínio
Destaques
Artigos
Berry Bank: Criando um Banco Digital Gamificado para seus Filhos com Gentoo, Flask e Tailscale
Papagaiando o XFCE com temas e recursos
Dicas
Instale o DOOM Retro no Gentoo facilmente via Overlay
Steam (Flatpak) rodando jogos em partição NTFS
O dock Plank + U-Launcher deixam qualquer desktop mais produtivo
Tópicos
Instalar Linux em notebook Sony Vaio VPCEG13EB (17)
Alguém tem que acabar com ANATEL!!! (10)
O que você está ouvindo agora? [2] (229)
Top 10 do mês
-

Xerxes
1° lugar - 129.078 pts -

Fábio Berbert de Paula
2° lugar - 59.363 pts -

Buckminster
3° lugar - 27.907 pts -

Sidnei Serra
4° lugar - 21.261 pts -
Alberto Federman Neto.
5° lugar - 20.932 pts -

Alessandro de Oliveira Faria (A.K.A. CABELO)
6° lugar - 20.013 pts -

Mauricio Ferrari (LinuxProativo)
7° lugar - 19.760 pts -

edps
8° lugar - 18.897 pts -

Daniel Lara Souza
9° lugar - 18.848 pts -

Andre (pinduvoz)
10° lugar - 17.137 pts